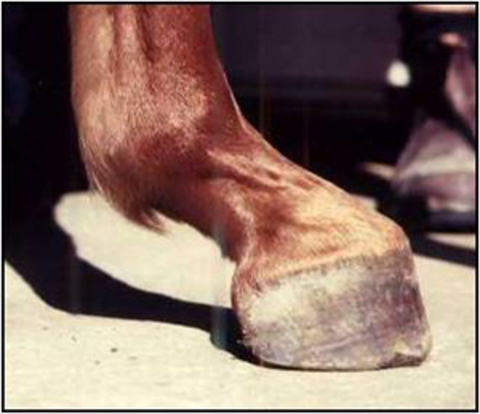
club foot horse definition
The hind foot on the same side of the horse as the club foot also has distinct characteristics that clearly distinguish it from the opposite hind foot. Unknown DM me for creditFollow and Tag horsesclubb for morehorse horses lovehorses eq.
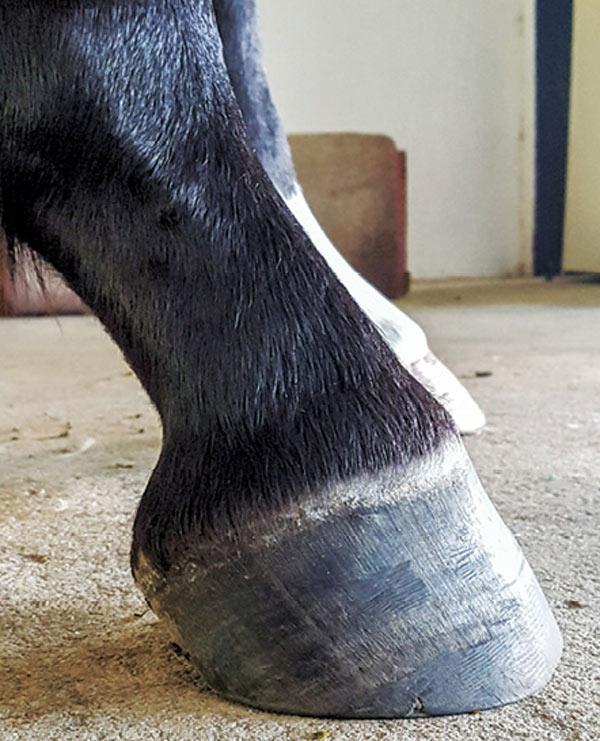
Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles
When the hoof angle of one foot is 3 to 5.

. On sound horses hooves tend to. This is the most common tendon flaw in foals. The contracted muscleclub foot condition is a common growth problem in young horses up to 6 months of age causing upright pasterns and a tiptoe stance.
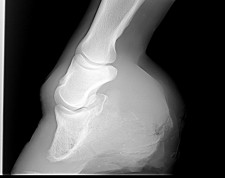
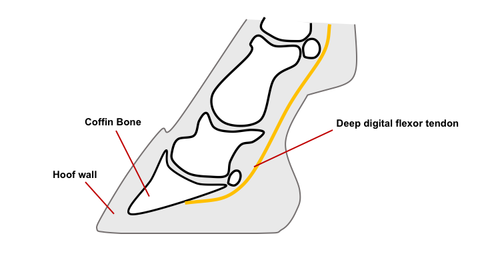
The calf muscles in the affected leg are usually underdeveloped. Thus it pulls on and rotates the coffin bone downward in the hoof. In the horse hoof growth is dictated in large part by weight distribution.
Cuteness overloadHow cute are they from 1 to 10. Horses affected with club foot develop a flexural deformity of the coffin joint due to a shortening of the musculotendinous unit that starts high up in the limb and inserts on the coffin bone in the foot resulting in an upright conformation of the foot. Club foot is defined by the UC Davis Book of Horses as a flexural deformity of the coffin joint resulting in a raised heel.
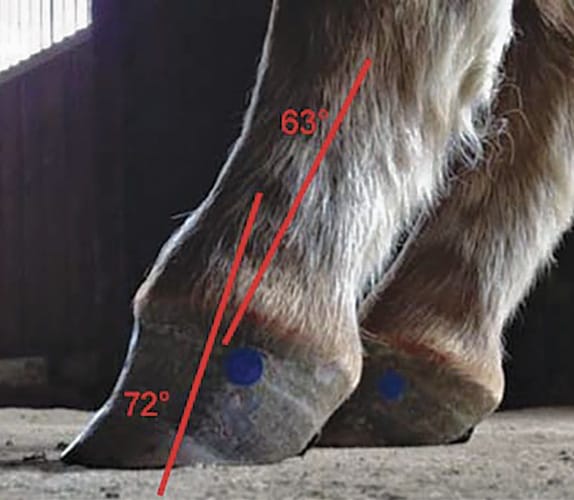
Club foot 60 deg or more Not uncommon to find feet that match on the diagonal. Juvenile Presentation The most frequently recognized form of clubfoot in horses occurs in sucklings or weanlings at approximately 2 to 8 months of age. In a club foot the angle of the hoof and pastern in relation to the ground is abnormally steep.
If discovered soon enough this condition can be reversed by altering the foals diet and reducing stress on. In the past the condition was defined as any hoof angle that exceeded 60 degrees but the reality is not quite that exact. After 11 months of gestation it is a costly and heart breaking exercise if it results in a club footed foal.
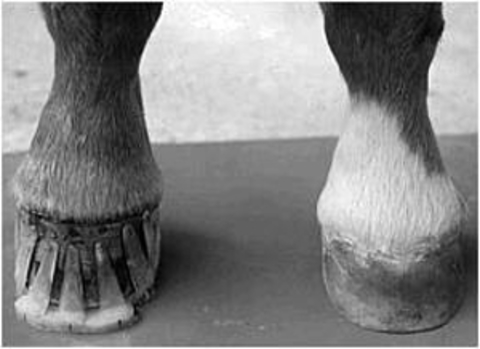
Generally the greater the upright angle the more severe the club foot. Several theories address the potential causes ranging from a genetic predisposition to hoof or body injury to improper trimming andor shoeing. The first clinical sign recognized is an upright appearance of the foot combined with the inability of the heels to contact the ground.
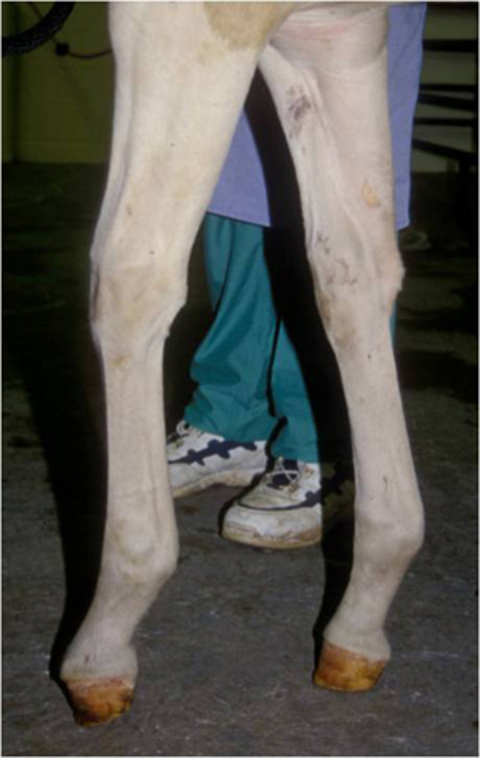
The affected leg or foot may be slightly shorter. The muscle belly that controls the deep digital flexor tendon is located high in the limb. A club foot alters a horses hoof biomechanics frequently leading to secondary lamenesses.
There are varying degrees of club foot. The only way to stop continuing problems with club footed horses is not to breed from them. This is often seen in foals with developmental problems due to rapid growth.
It is important to understand the difference and spot a club foot early in a foals life. An upright foot is not the same as a club foot. A normal angle for a horses hooves varies by the individual.
If a horse puts more weight on the inside of a hoof the blood is pushed to the opposite side of the foot causing faster growth and wearing down the weighted surface at a faster rate. Yes those are all four club feet First off not singling you out. Not to be confused with the club foot deformity of.
The deep digital flexor tendon DDFT is much shorter than the bones. Omg this horse is crazy but also so braveHow much braveness has your horse from 1 to 10. Equine club foot has several distinguishing characteristics Don says.
Even the hind foot that follows a grade 1 club will have a lower profile hoof angle lower heel and less than healthy digital cushion depth much like that of the low heel in front. AhorsesworldFollow horsesclubb for morehorse hor. In Standardbreds the H-L zone normally is a little wider averaging 20 mm.
Fixing a club foot requires relief of the underlying tendon-ligament stresses causing the flexural deformity. Though the angles are quite high it looks as though the right front and left hind may be low grade club feet. Club feet are surprisingly common with up to 60 of the domestic horse population exhibiting at least minor characteristics.
Just answering multiple posts from here. The foot may be turned so severely that it actually looks as if its upside down. With respect to the club foot the heel of the affected foot grows faster and the hoof.
Affected horses tend to land toe-first and their heels growth rate is amplified relative to the. Club foot refers to a limb flaw where the hoof is very upright with a long heel. 1-36-8 It is commonly a unilateral condition but occasionally affects both limbs.
In general club foot most commonly occurs in the front legs. Normal H-L zone width for Warmbloods depends on the size of the foot. Normal dorsal H-L zone width in Quarter Horses Thoroughbreds and most other light horse breeds is 15 - 16 mm.
The normal range of hoof angle is 50 to 55 degrees while a club foot might stand at more than 60 degrees. A matter of degree. A club foot is a DEFORMITY and for any horse to win at top level competition it needs every possible advantage and no drawbacks.
The top of the foot is usually twisted downward and inward increasing the arch and turning the heel inward. In many cases it is similar to that for light breeds.

Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles
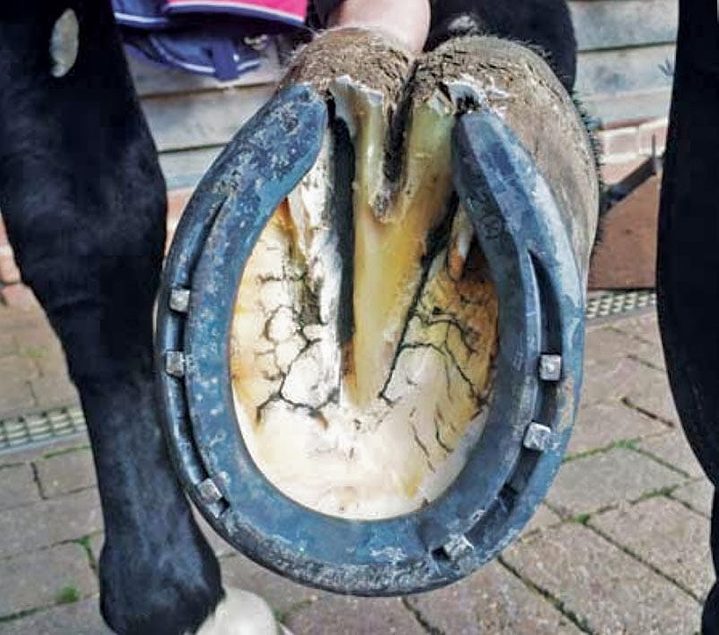
Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot

Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome

Ballerina Syndrome Where The Heels Remain Off The Ground Even At The Download Scientific Diagram

The Club Foot Is It No Big Deal Or A Deal Breaker
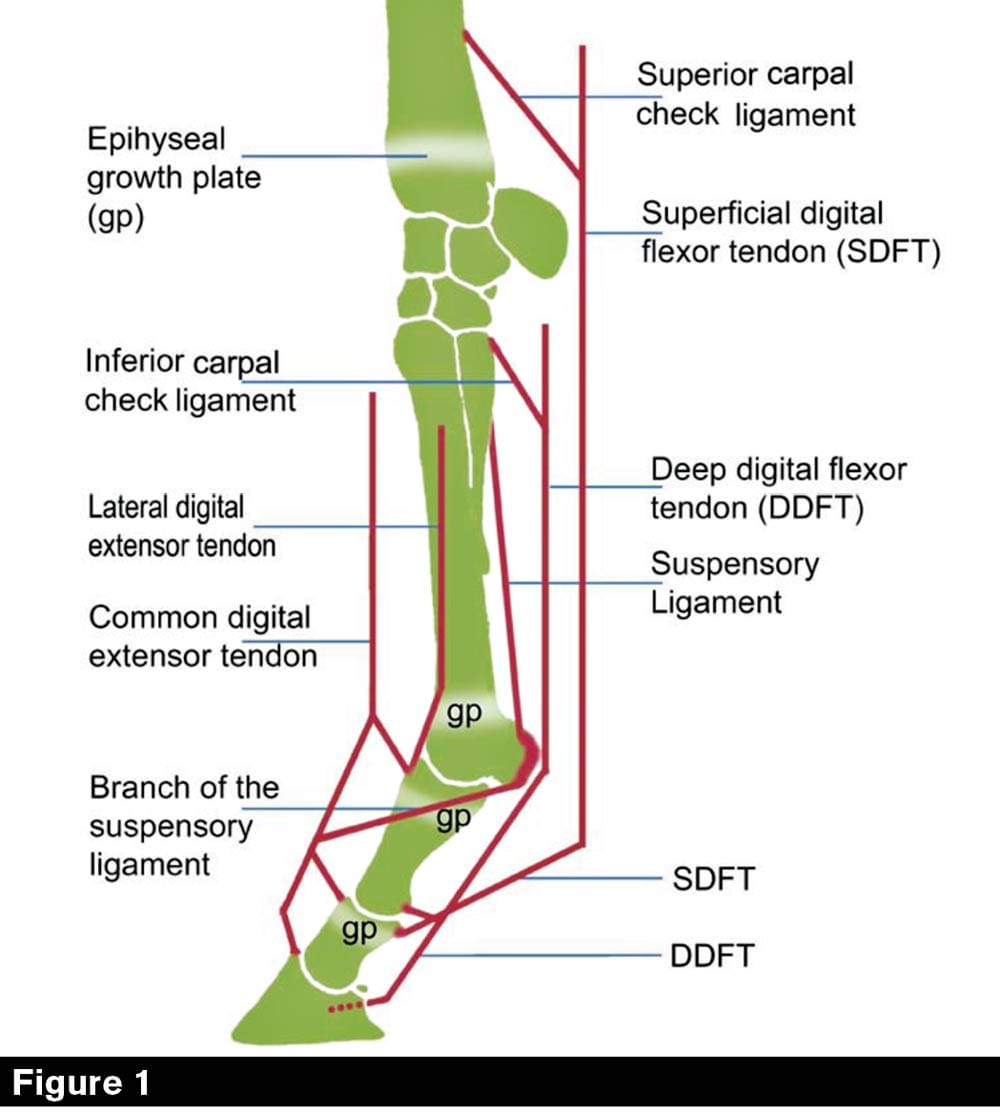
Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot

Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome

Recognizing Various Grades Of The Club Foot Syndrome
Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot
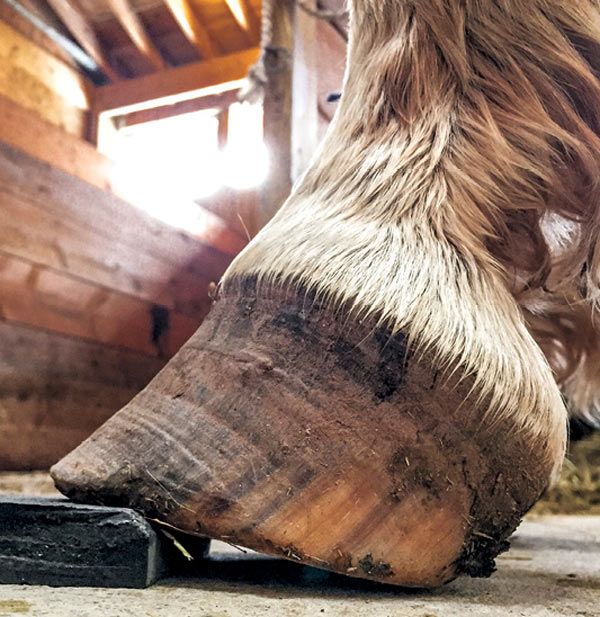

Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles
Blog Okanagan School Of Natural Hoof Care